Keywords are words and phrases that people use when typing into a search engine.
It is very important for SEO to include keywords in your titles and text so that both people and search engines know what your content is about.
If you target good keywords and use them in the right way, then it will help you get more traffic from search engines.
Keywords are important for SEO

The acronym “SEO” stands for Search Engine Optimization.
In SEO, keywords are the words and phrases in your content that make it possible for users to find your content via search engines.
By doing keyword research and optimization, you ensure that your content uses the same language as your potential visitors do when searching for stuff online.
In this way, keywords are what search engines use to bridge the gap between your content and search engine users.
Without the right keywords, search engines may not realize that your content is a good fit for people’s search queries.
Plus, even if your site were to show up in the search results, people are less likely to click on it if it doesn’t contain the words and phrases they have in mind.
Because of this, keywords have been a core component of SEO since the early days of the search engines.
Even though search engines have become better at understanding synonyms and context, keywords are still an important aspect of modern SEO.
Bottom Line: Keywords are important in SEO because they show both search engines and users what your content is about. Keywords use the same language as your potential visitors when they search for stuff online.
An example of keyword use in SEO
Below is an example of really effective keyword use in an article about green tea.
I wrote this article myself and it has ranked #1 for “green tea”, “green tea benefits” and other related high-traffic keywords for a long time.
Here’s a screenshot that shows how keywords are used in the title and text:
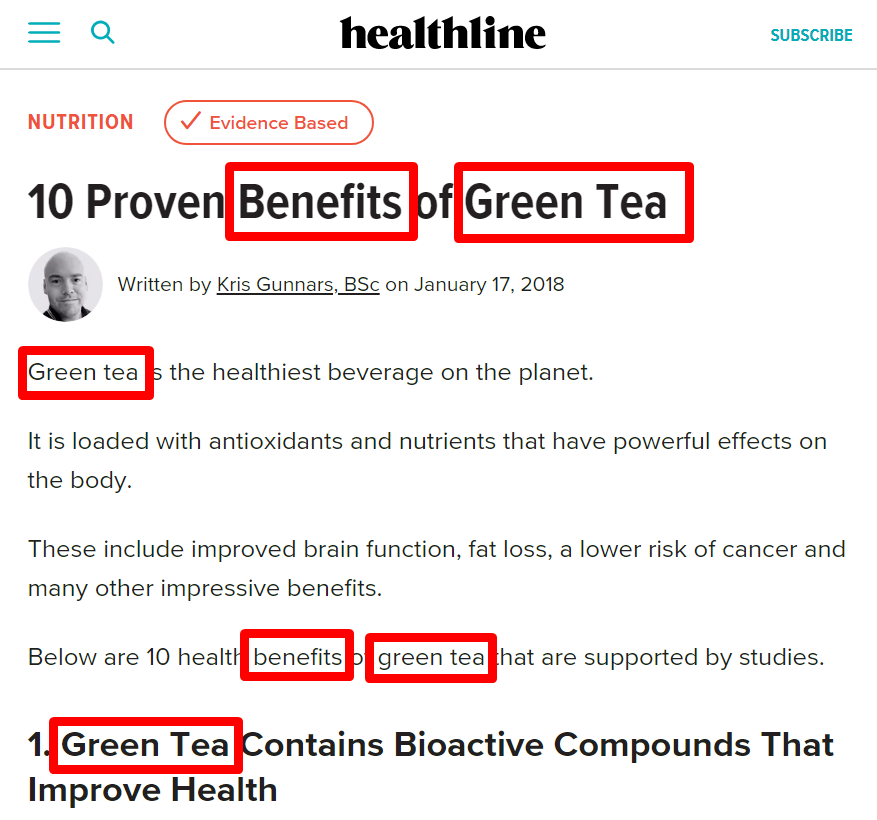
Take note of how the keywords are used sparingly in a way that looks natural. There is no keyword stuffing going on here, which is more harmful than helpful.
In addition, Google ranks the article for many other keywords that it sees as being related to the main keywords or relevant to the article. According to SEMRush, the article ranks for a total of 2,692 keywords in the US alone.
Because of this, you don’t need to specifically target all the different ways that people might find your article. Just write a comprehensive article in a natural way and Google will rank your article for many different search queries.
This is what the search engine result looks like when you type “green tea” into Google:
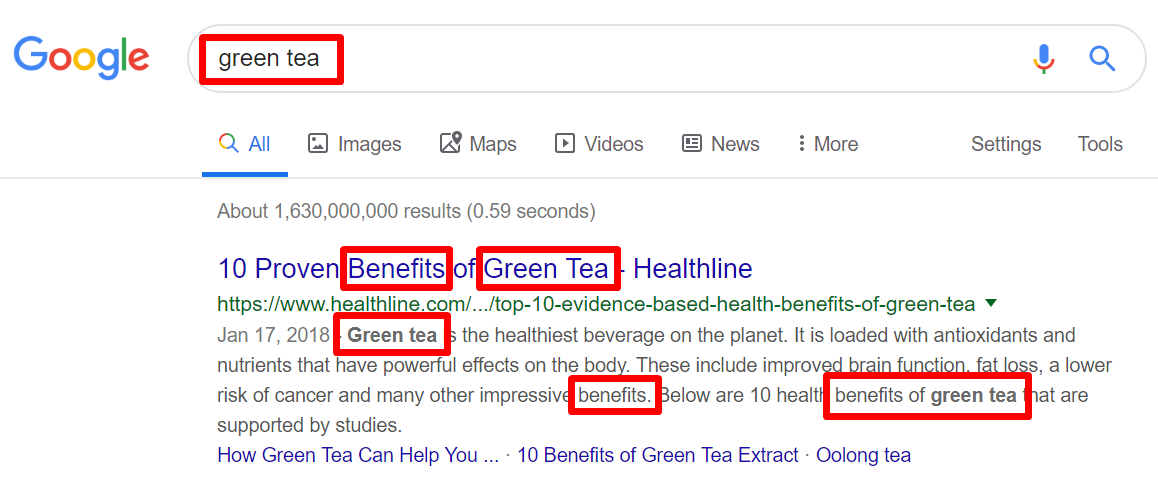
You can see that the keywords are used in a natural way and the title clearly tells both users and search engines what the article is about.
In total, this article has gotten over 13 million visits and is still getting thousands of visits each day. This would have been impossible without proper keyword use.
Bottom Line: Using keywords in your title and text can help your site rank in search engines when people search for the terms. But you can also rank for many other keywords that are seen as being related or relevant.
Short-tail vs long-tail keywords
Keywords are often categorized as being either “short-tail” or “long-tail.”
This is often defined based on the number of words in the keyword phrase. If the phrase has only 1-2 words, like “dog” or “dog food,” then it is considered to be a short-tail keyword.
But if the keyword phrase has 3 or more words, such as “best dog food for a labrador,” then it is considered to be a long-tail keyword.
Short-tail vs. long-tail is also defined based on search volume. The short-tail terms get the most traffic, while the long-tail terms get less traffic but also tend to be easier to rank for.
Long-tail terms also tend to have higher conversion rates for commercial search queries.
Here’s a diagram from SEMRush that shows this concept visually. The high-traffic, short-tail terms are on the left, with the low-traffic, long-tail terms on the right.
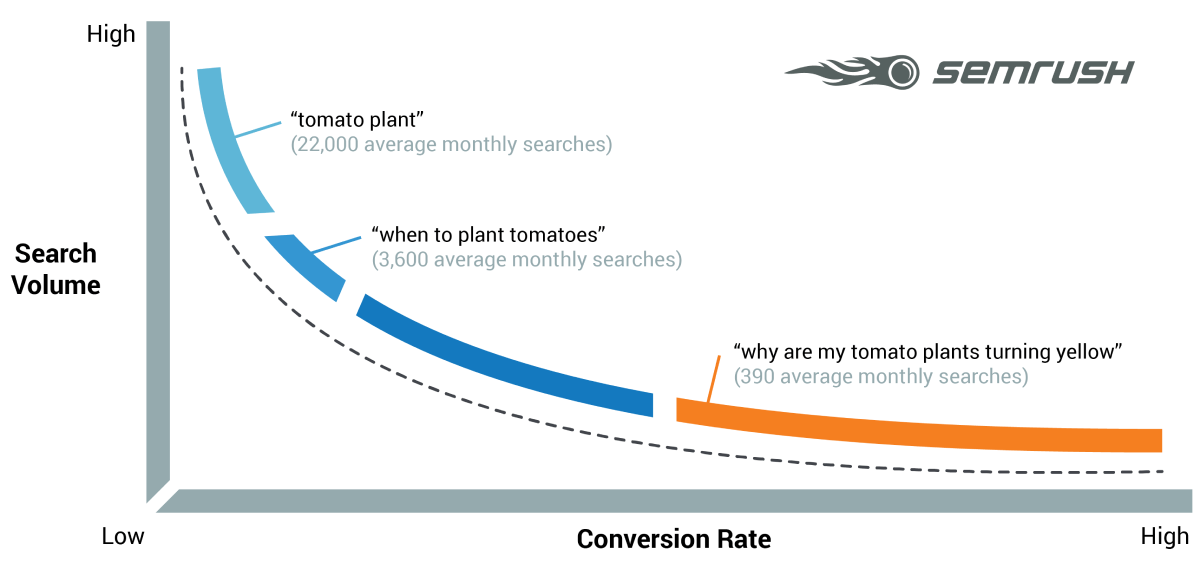
All things being equal, long-tail terms have less competition and are easier to rank for. This is particularly true for sites that are new and don’t have a lot of authority in Google’s eyes yet.
To go back to the green tea example, “green tea” is a very high-traffic, short-tail keyword with a lot of competition. It would be almost impossible for a new site to rank for this term.
But a long-tail keyword phrase like “is green tea good for weight loss” is much easier to rank for but still has a decent amount of search volume.
It is important to target keywords where you have a chance of being able to rank.
Bottom Line: Keywords are often categorized as long-tail or short-tail, depending on the search volume and the number of words in the phrase. Long-tail terms are generally easier to rank for.
How to do keyword research
Keyword research is exactly what the name implies, doing research on keywords to target in your content.
I prefer to do keyword research before I even start writing. Then I know what language to use in my articles to make it easier for people to find my stuff via a search engine.
Most people do keyword research by adding a word into a keyword tool and looking at three factors:
- Search volume: The estimated number of searches per month.
- Competition: How competitive the keyword is and how hard it is to rank for.
- Related keywords: Words and phrases that are related to the keyword you typed in.
Here’s a screenshot from the Keyword Tool in SEMRush. You can see how typing in a seed keyword brings up related keywords, their search volume, and the keyword difficulty (KD).
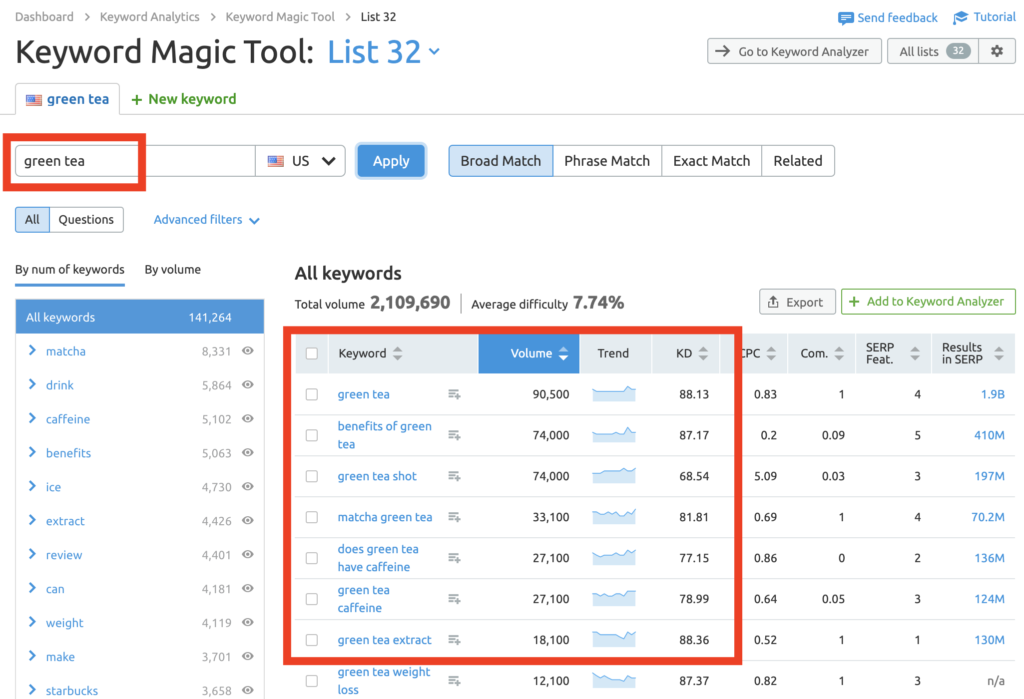
You can also enter the URL of a competitor into a keyword tool and see which keywords they rank for.
One of the goals of keyword research is to find words and phrases that have moderate- to high search volume but little competition.
Chances are that your main keyword won’t fit that profile, but one of the related keywords might.
When you find good keywords that you think you could rank for, then it makes sense to put them in a spreadsheet for later use.
To get started, here are a few keyword tools you can use:
- SEMRush (paid with a free 7-day trial)
- aHrefs (paid)
- Moz Pro (paid)
- KWFinder (paid)
- KeywordTool.io (paid)
- Google Ads Keyword Planner (free)
- UberSuggest (free)
- Keywords Everywhere (free)
Keyword research is also important for search engine marketers who drive traffic with paid search ads. Just like organic search, paid search is also highly dependent on keywords.
Bottom Line: Keyword research involves finding good keywords with moderate- to high search volume, but relatively little competition.
How and where to use keywords for SEO
Finding the right keywords is essential, but it won’t do you much good unless you also know how and where to use the keywords for optimal SEO results.
Using keywords properly is part of on-page SEO, the type of SEO that happens on the page that is intended to rank.
Here are several places to include your keywords for effective on-page SEO:
- Title tag: Write an interesting but accurate title that includes your main keywords.
- H1 tag: Also include them in the main heading (h1) of the page. You can make this identical to your title tag if you want.
- Meta description: Write a description that makes it clear that your article answers the intent of people who are searching for the keyword.
- URL: It often makes sense to include the main keyword in some form in the URL.
- Content: Include your keywords and their synonyms inside the text. Don’t aim for a specific “keyword density” — just write naturally.
- Image alt tags: Write descriptive alt tags for your images. If a natural description happens to include one of your keywords, then that’s great.
- Subheadings: Sometimes it makes sense to include the main keywords in one or more subheadings (h2, h3, etc).
- Internal anchor text: When linking to this page from other pages of your site, try using anchor text that is related to the main keywords.
Keep in mind that you don’t need to use the exact match of your primary keyword each time. This can look unnatural, especially for long-tail keywords.
Instead, use synonyms, fragments, and natural variations of your main keywords throughout the text.
For example, if you are writing about a long-tail phrase like “is green tea good for weight loss,” then it will look strange if you include that exact phrase many times.
Instead, use words like “green tea,” “weight loss,” “lose weight,” etc. naturally throughout the text and the search engines will understand what it is about.
Most importantly, write your text for people, not search engines.
Bottom Line: Using your keywords on the page is part of on-page SEO. Best practices include using some forms of the keywords and their synonyms naturally in the title, main heading, description, URL and throughout the content.
Content quality is still critical
Including the right keywords is just one part of SEO. It is unlikely to drive a lot of traffic on its own.
You also need to make sure that your content is of exceptionally high quality and that it fulfills the intent of people searching for the keywords on Google.
In addition, the keywords you choose to target should be relevant to the main topics of your site.
At the end of the day, what Google wants is to give people the best answers to their search queries.
Keywords are necessary to establish relevance, but the quality of your content is what will determine whether you end up getting search traffic or not.